Publications
Study on the decompression behaviour during large-scale pipeline puncture releases of CO2 with various N2 compositions: Experiments and mechanism analysis
Yu, S., Yan, X., He, Y., Chen, L., Hu, Y., Yang, K., ... & Chen, S. (2024). Study on the decompression behavior during large-scale pipeline puncture releases of CO2 with various N2 compositions: Experiments and mechanism analysis. Energy, 296, 131180. Access the publication here Impurities in the captured CO2 stream from various industrial sources may introduce uncertainty into the transient releases of transportation pipelines. Due to limitations in the experimental scale, there is...
Estimating the line packing time for pipelines transporting carbon dioxide
Martynov, S. B., Porter, R. T., & Mahgerefteh, H. (2024). Estimating the line packing time for pipelines transporting carbon dioxide. Carbon Capture Science & Technology, 11, 100188. Abstract During the operation of pressurised pipelines transporting compressible fluids, line packing is employed as an effective method that uses the pipeline itself as a buffer storage, compensating for fluctuations in the fluid supply or demand. While in large-capacity natural gas transmission systems,...
Experimental study on supercritical CO2 jet characteristics and coal breakage utilization in carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS) process
Hu, Y., Chen, L., Cao, Z., Yang, K., Yan, X., & Yu, J. (2024). Experimental study on supercritical CO2 jet characteristics and coal breakage utilization in carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS) process. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 184, 260-270. Access the publication here In the framework of Global Warming strategies, the safe utilization of carbon dioxide (CO2) is an important component of the Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) process. In the...
Study on the leakage morphology and temperature variations in the soil zone during large-scale buried CO2 pipeline leakage
Yu, S., Yan, X., He, Y., Yu, J., & Chen, S. (2024). Study on the leakage morphology and temperature variations in the soil zone during large-scale buried CO2 pipeline leakage. Energy, 288, 129674. Access the publication here In the CCUS technology chain, buried CO2 pipelines are inevitable under special terrain conditions. Due to the concealment and the complexity of the soil, they have a higher possibility of leakage. However, there is limited research on buried CO2 pipeline...
Experimental study of decompression wave characteristics and steel pipe applicability of supercritical CO2 pipeline
Chen, L., Hu, Y., Yang, K., Yan, X., Yu, S., Yu, J., & Chen, S. (2024). Experimental study of decompression wave characteristics and steel pipe applicability of supercritical CO2 pipeline. Gas Science and Engineering, 121, 205203. Access the publication here High-strength pipeline steel is the optimal choice for continuously transporting large amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the future Carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS) industrial chain, and supercritical CO2 (S–CO2) is the...
Experimental Proof of Concept of Blast Furnace Gas Decarbonisation via CASOH Process
Publication: Experimental Proof of Concept of Blast Furnace Gas Decarbonisation via CASOH Process 2022. Grasa, C. Navarro, J. R. Fernández, , M. Diaz, M. Alonso, A. Amieiro, S. Poultson, J. Brandt, J. C. Abanades. Experimental Proof of Concept of Blast Furnace Gas Decarbonisation via CASOH Process. Proceedings of the 16th Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies Conference (GHGT-16) 23-24 Oct 2022. October 2022, Lyon, France. Grasa et al presented ‘Experimental proof of concept of Blast Furnace...
An MINLP model for the optimal design of CO2 transportation infrastructure in industrial clusters
Ejeh, J. O., Martynov, S. B., & Brown, S. F. (2023). An MINLP model for the optimal design of CO2 transportation infrastructure in industrial clusters. In Computer Aided Chemical Engineering (Vol. 52, pp. 3085-3090). Elsevier. Access the publication here Carbon capture, utilisation and storage (CCUS) is still the most promising decarbonisation route for carbon-intensive sectors. In the context of industrial clusters, although benefits exist from economies of scale and shared...
The Ca-Cu looping process using natural CO2 sorbents in a packed bed: Operation strategies to accommodate activity decay
The Ca-Cu looping process is a promising CO2 capture technology designed to produce H2 and power from a fuel gas. The use of inexpensive and widely available limestone would facilitate the scale up of this technology. This work proposes a novel strategy for packed-bed Ca-Cu looping processes consisting of loading the sufficient amount of CuO to calcine only a well-defined fraction of CaCO3 in every cycle during the transient period until the limestone reaches a residual solid conversion of...
Puncture Failure Size Probability Distribution for CO2 Pipelines
The safe operation of pressurised CO2 pipelines is key to the success of Carbon Capture and Storage as a viable means for tackling global warming. However, given their relatively small number currently in operation, the confident prediction of their puncture size failure probability and how it compares with hydrocarbon pipelines are fundamentally important questions that must be resolved. This paper presents the development and application of a robust statistical analytical technique for the...
Multi-objective economic and environmental assessment for the preliminary design of CO2 transport pipelines
A methodology based on the multi-objective optimisation of economic and environmental aspects is presented to support the preliminary design of CO2 transport pipelines employed as part of Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) systems. Pareto optimal design solutions are determined for a realistic point-to-point CO2 pipeline using Level Diagrams and choosing the Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) as a decision variable. A quantitative procedure entailing the definition of economic and environmental key...
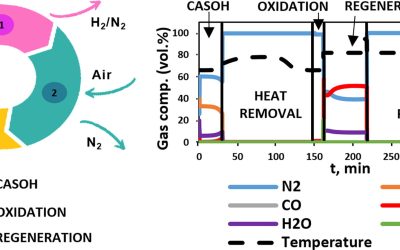
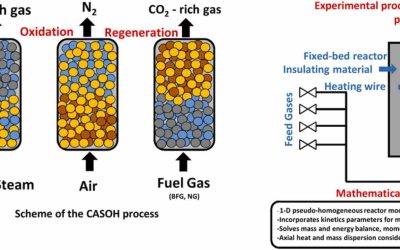
Blast furnace gas decarbonisation through Calcium Assisted Steel‐mill Off‐gas Hydrogen production. Experimental and modelling approach
The Calcium Assisted Steel-mill Off-gas Hydrogen production process (CASOH) is able to upgrade and decarbonise blast furnace gases (BFG), which is the main source of CO2 emissions in integrated steel making plants. The three main reaction stages of the process (i.e. H2 production via calcium-assisted water-gas-shift of BFG, Cu oxidation and CO2 sorbent regeneration) have been investigated in a lab-scale fixed bed reactor, using readily available functional materials (i.e. a commercial Cu-based...
Blast furnace gas utilisation with Ca-Cu looping cycle for hydrogen-enriched syngas production
Access the conference publication here! During the 9th High Temperature Solid Looping Cycles Network Meeting, Navid Khallaghi (University of Manchester) presented the techno-economic evaluation of the blast furnace gas utilization with Ca-Cu looping cycle for hydrogen-enriched syngas production. The study showed the potential of the Calcium Assisted Steel-mill Off-gas Hydrogen (CASOH) production, at 10 bar and 753°C, by combining the Ca-Cu looping with the sorption enhanced water gas shift...